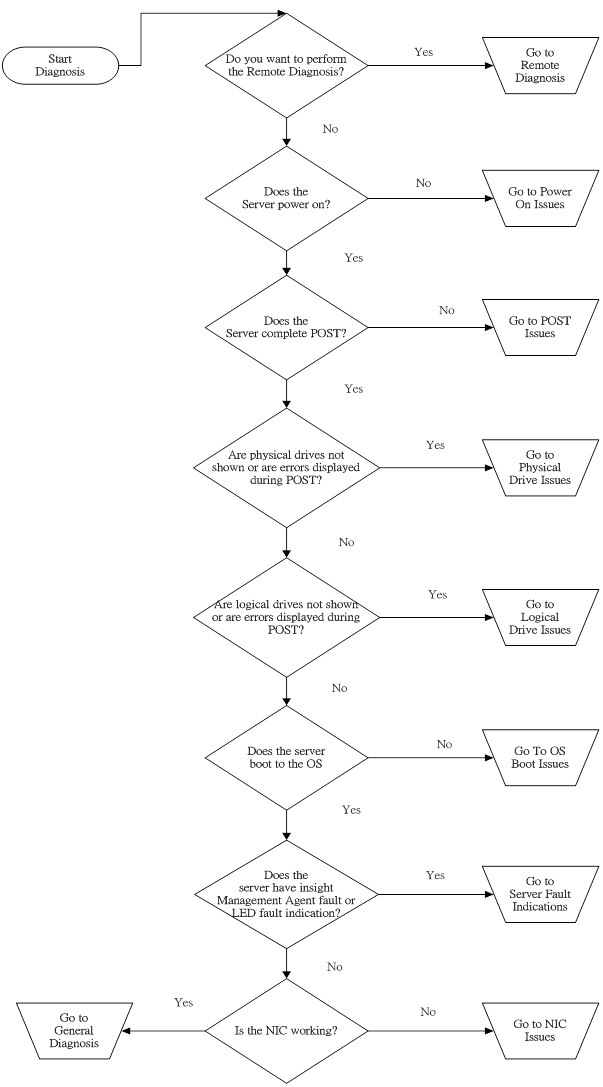
Use the following flowchart to start the diagnostic process:

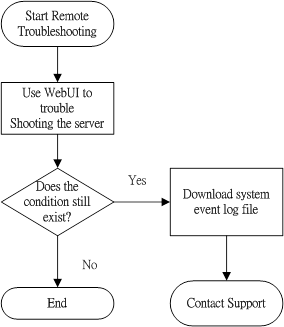
The Remote diagnosis flowchart provides a generic approach to troubleshooting a server from a remote location.

For the location of server LEDs and information on their statuses.
Symptoms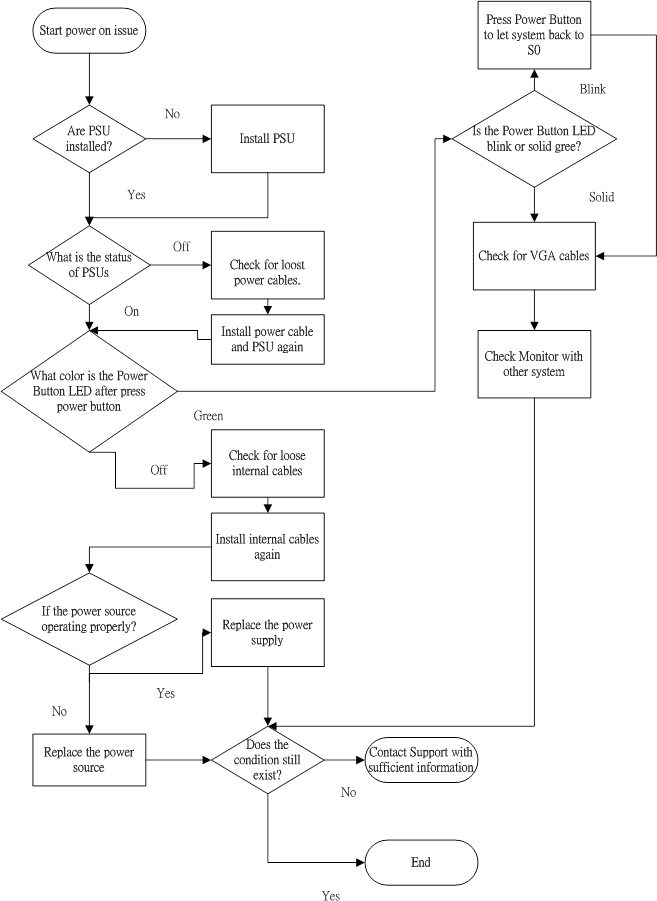
Symptoms
- The server does not power on.
- The system power button LED is off or Green blinking.
- Improperly seated or faulty power supply
- Loose or faulty power cord
- Power source issue
- Improperly seated component or interlock issue
- Troubleshoot the issue using the following flowcharts:

Symptoms
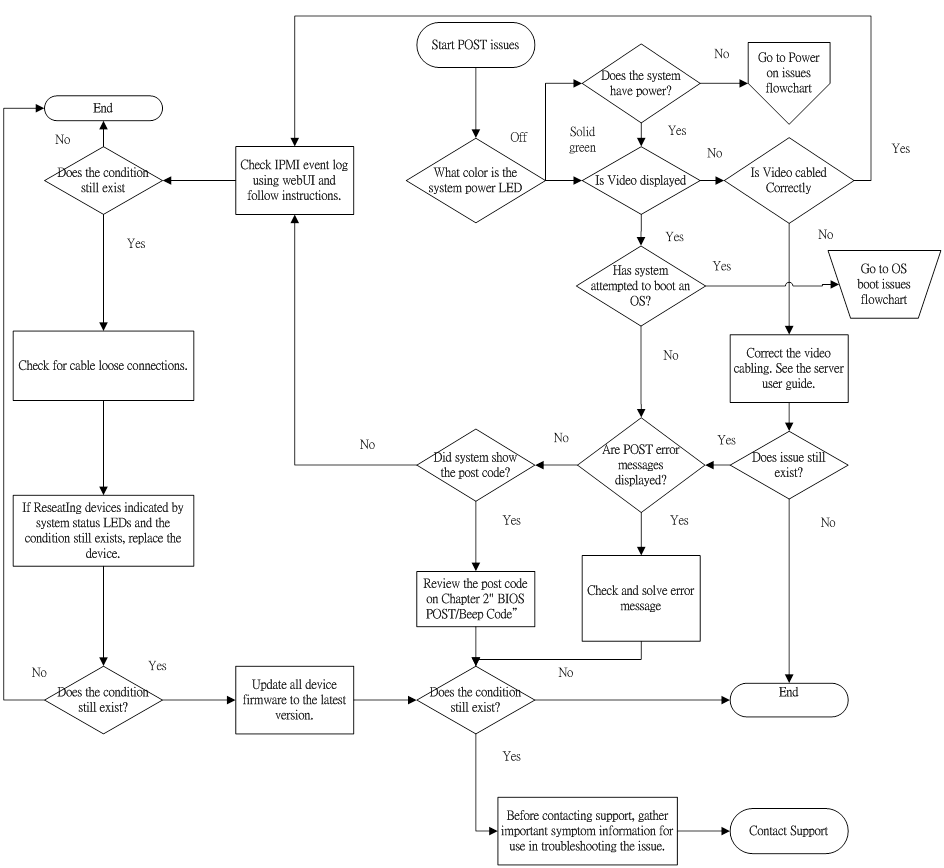
- The server does not complete POST.
- The server completes POST with errors.
- Improperly populated memory
- Outdated firmware on adapter options
- Unsupported adapter
- Improperly seated or faulty internal component
- Faulty video device
- Troubleshoot the issue using the following flowcharts:

Symptoms
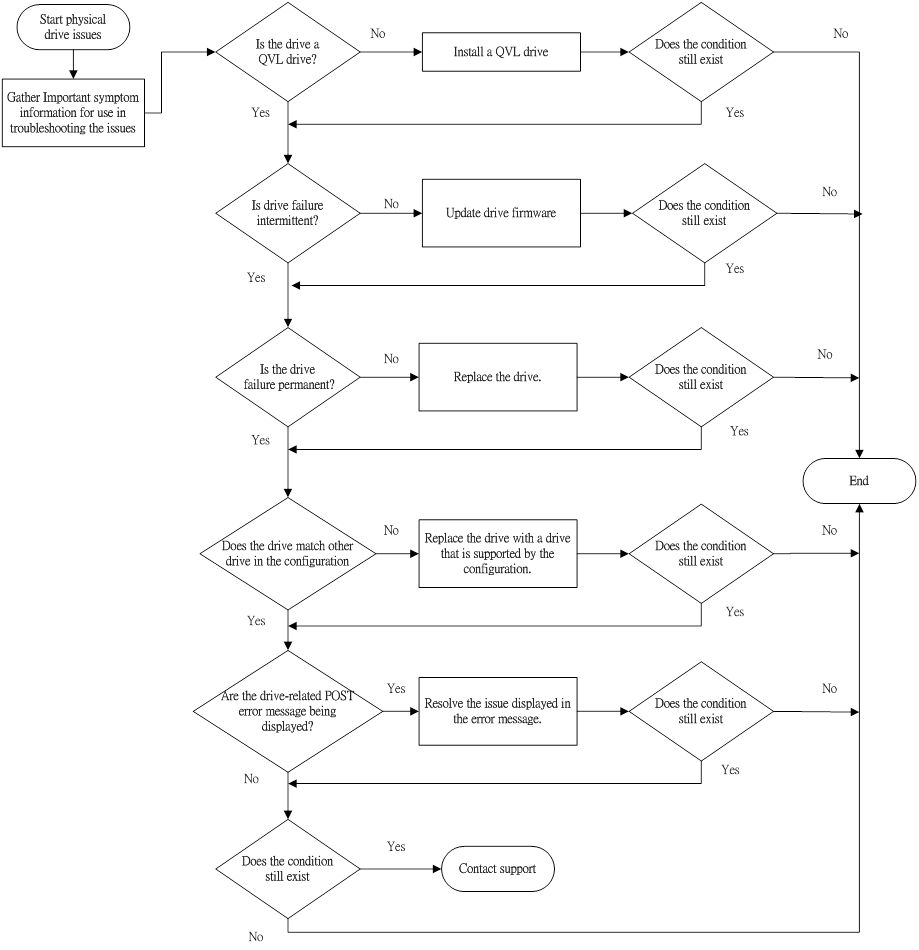
- A drive is not available.
- Drive errors are displayed during POST in the logs.
- The drive is faulty.
- The firmware is outdated.
- The drive does not match other drives in the same configuration.
- Troubleshoot the issue using the following flowcharts:

Symptoms
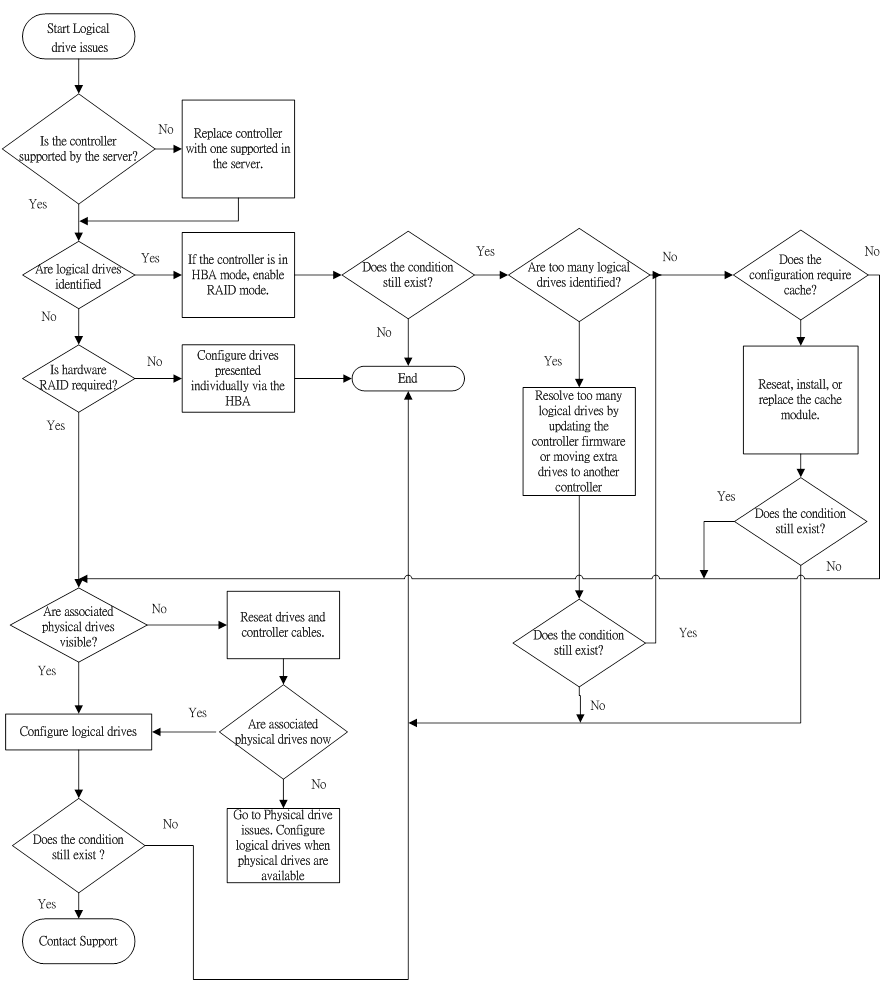
- Logical drive errors are displayed during POST or in one of the logs.
- The logical drives associated with an array controller are not visible during POST.
- The controller is not in RAID mode.
- The drives or cables are not seated properly.
- The associated physical drives are not available.
- Logical drives are configured.
- Troubleshoot the issue using the following flowcharts:

Symptoms
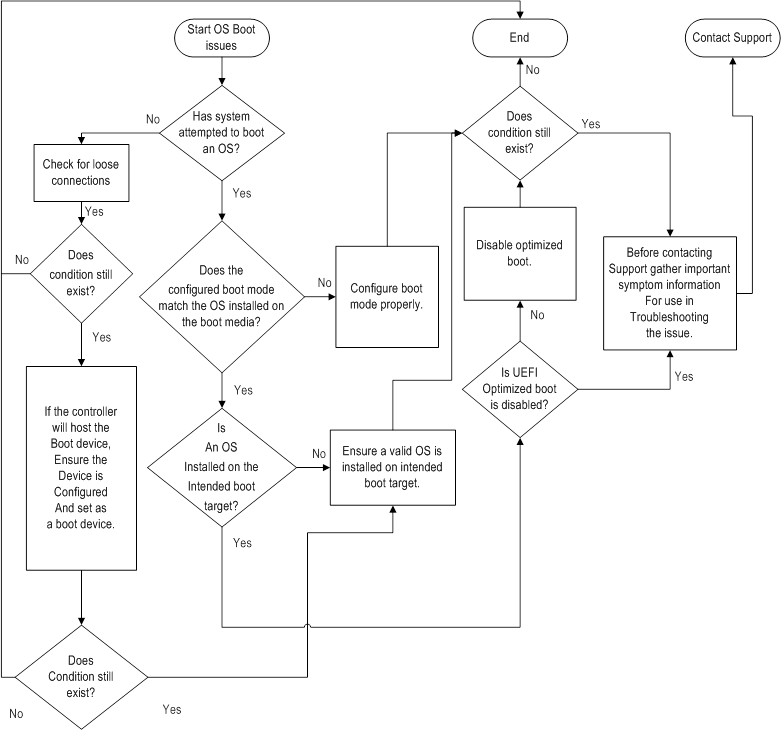
- The server does not boot a previously installed OS.
- Corrupted OS.
- Drive subsystem issue
- Incorrect setting in BIOS
- Troubleshoot the issue using the following flowcharts:

Symptoms
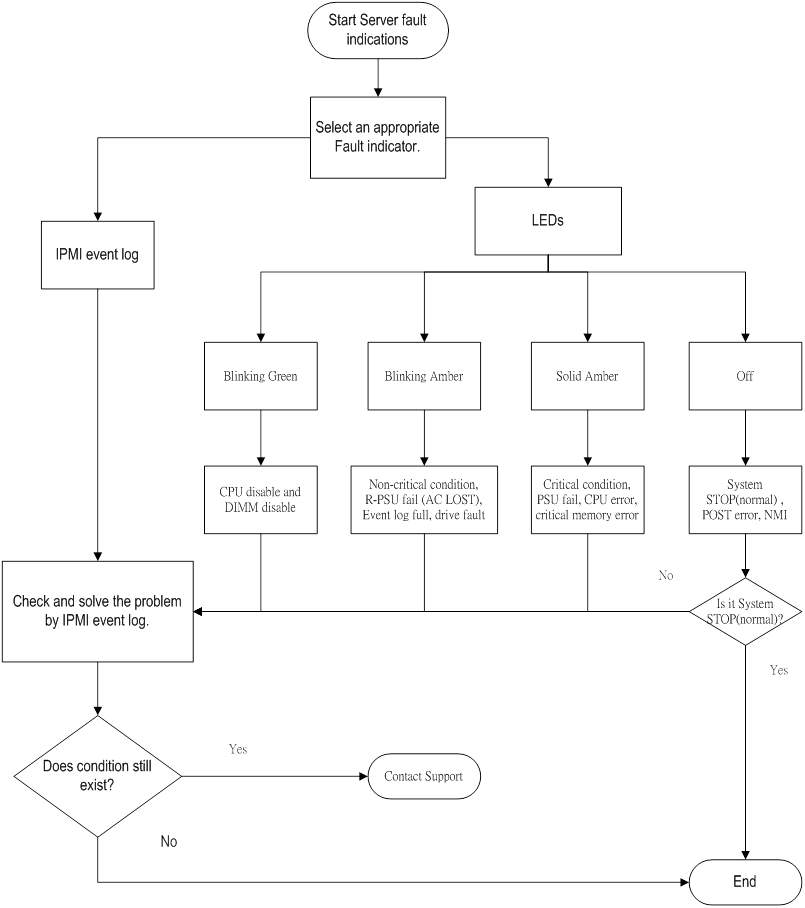
- The server boots, but the System Status LED is amber or Blinking Green.
- The server boots, but a fault event is reported by BMC.
- Improperly seated or faulty internal or external component.
- Unsupported component installed.
- Redundancy failure.
- System over temperature, over voltage condition, or over lower speed condition of FAN.
- Processor or memory error.
- BMC event log full.
- Troubleshoot the issue using the following flowcharts:

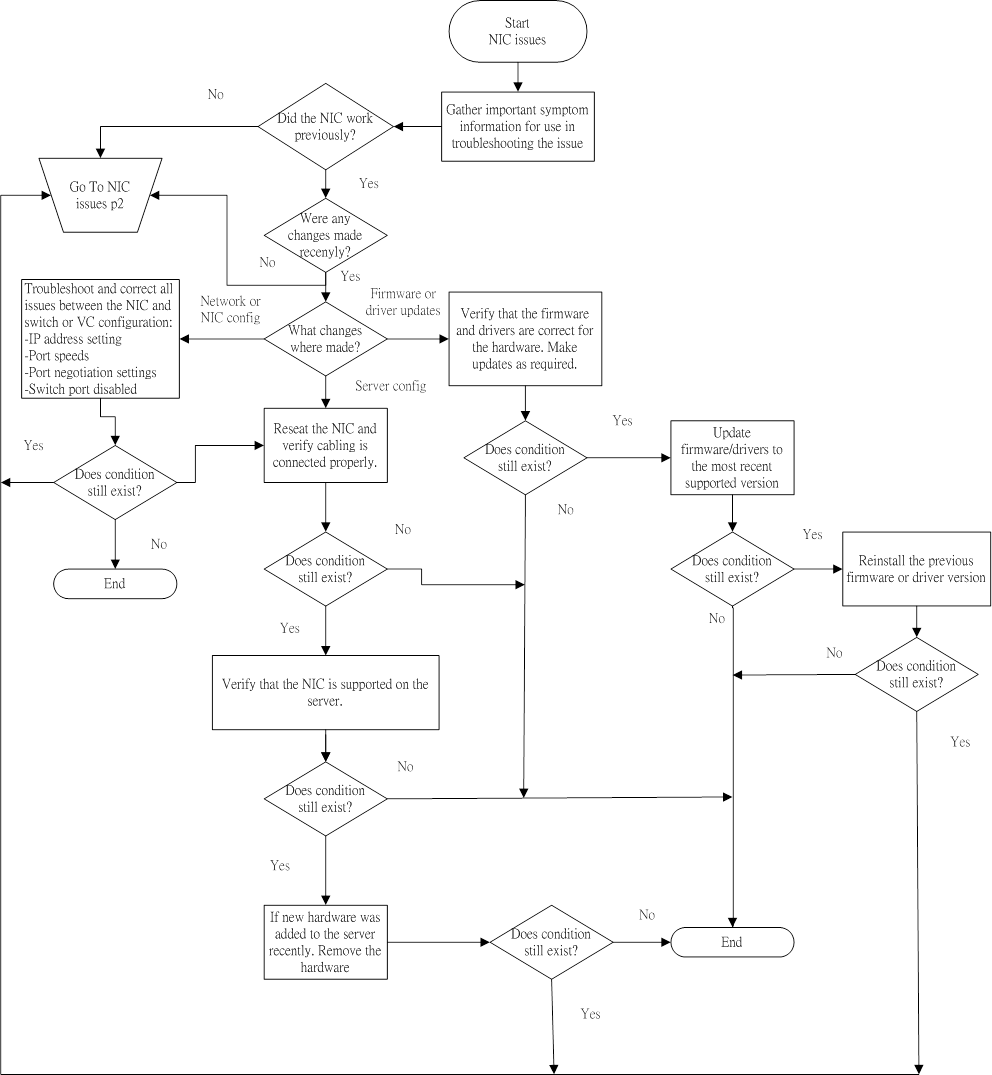
Symptoms
- The NIC is not working
- One or more ports on the NIC is not working.
- The firmware or drivers are outdated, mismatched, or faulty.
- The NIC or cable is not seated properly.
- The NIC, the cable, or other hardware is faulty.
- The hardware components are not supported in the same configuration.
- The NIC is not supported on the server.
- NIC issues flowchart (1 of 2)
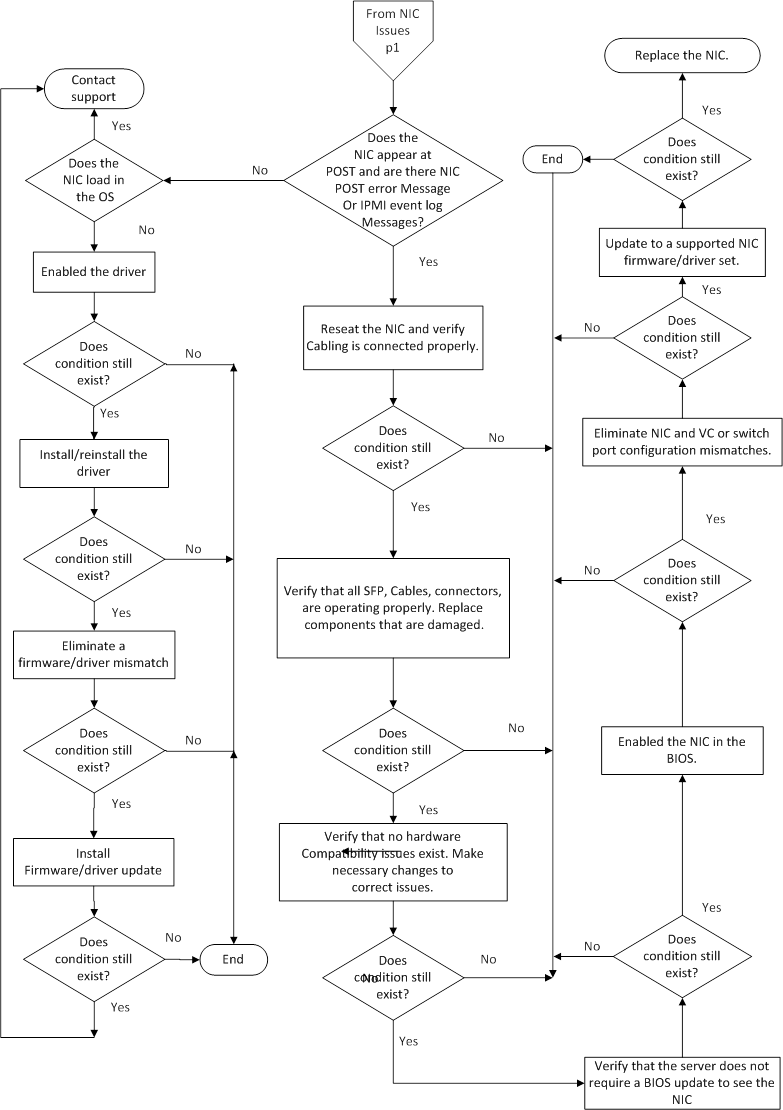
- NIC issues flowchart (2 of 2)
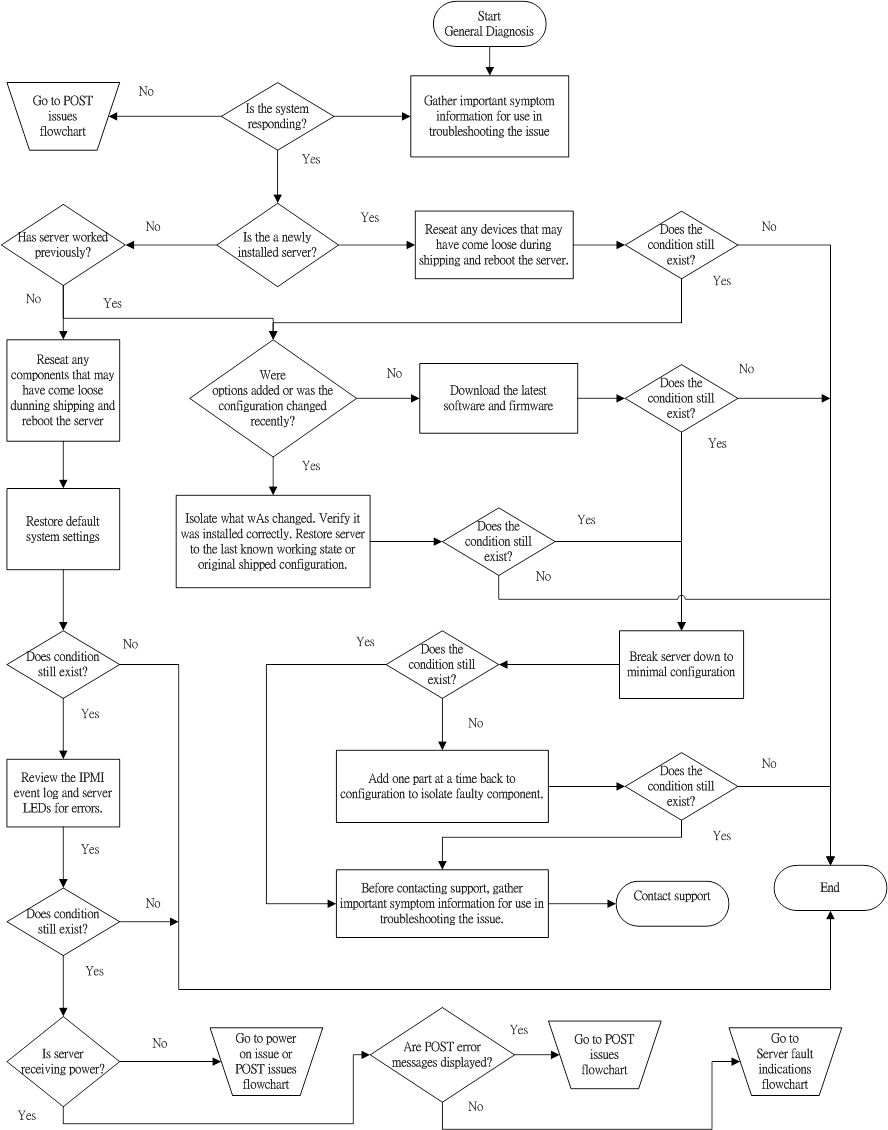
The General diagnosis flowchart provides a generic approach to troubleshooting. If you are unsure of the issue, or if the other flowcharts do not fix the issue, use the following flowchart:

Symptom
- The system does not power on.
- Check with Power On issue flowchart.
Cause
- The server is not powered on.
- Components or cables might not be properly connected or seated.
- The grounded power outlet is not working.
- The power cord is not functional.
- The power strip is not functional.
- The circuit breaker is in the off position.
- The line voltage is insufficient for the load.
- Sufficient power is not allocated to support the server.
- Press the Power button to be sure it is on. If the server has a Power button that returns to its original position after being pressed, be sure you press the switch firmly.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Plug another device into the grounded power outlet to be sure the outlet works. Also, be sure the power source meets applicable standards.
- Replace the power cord with a known functional power cord to be sure it is not faulty.
- Replace the power strip with a known functional power strip to be sure it is not faulty.
- Be sure the proper circuit breaker is in the On position.
- Have a qualified electrician check the line voltage to be sure it meets the required specifications.
- Be sure there is sufficient power allocation to support the server.
Cause
- The power supply might not be fully seated.
- AC power is unavailable.
- The power supply failed.
- The power supply is in standby mode.
- The power supply has exceeded the current limit.
- The power supply is not supported on the server.
- The power is not sufficient for the hardware installed.
- Redundant power supplies are configured but the power supplies are not compatible.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- If the power supplies have LEDs, be sure they indicate that each power supply is working properly.
- If the LEDs indicate an issue with a power supply (red, amber, or off), then check the power source.
- If the power source is working properly, then replace the power supply.
- Be sure the system has enough power, particularly if you recently added hardware, such as drives. Remove the newly added component and if the issue is no longer present, then additional power supplies are required.
- If running a redundant configuration, be sure that all of the power supplies in the system have the same part number and are supported by the server.
Cause
- Unsupported hardware.
- Incomplete population of a memory bank.
- Connection of the data cable, but not the power cable, of a new device.
- Be sure the hardware being installed is a supported option on the server.
- If necessary, remove unsupported hardware.
- Be sure the issue is not caused by a change to the hardware release. For more information, see the release notes included with the hardware.
- Be sure the new hardware is installed properly. To be sure all requirements are met, see the device, server, and OS documentation.
- Be sure no memory, I/O, or interrupt conflicts exist.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Be sure all cables are connected to the correct locations and are the correct lengths.
- Be sure other components were not accidentally unseated during the installation of the new hardware component.
- Be sure all necessary software updates, such as device drivers, ROM updates, and patches, are installed and current, and the correct version for the hardware is installed. For example, if you are using a RAID controller, you need the latest RAID Controller device driver. Uninstall any incorrect drivers before installing the correct drivers.
- After installing or replacing boards or other options, verify that the system recognizes all changes to the hardware in the BIOS or in the options setup in UEFI System Utilities. If the new hardware is not configured properly, you may receive a POST error message indicating a configuration error.
- Be sure all switch settings are set correctly.
- Be sure all boards are properly installed in the server.
- Uninstall the new hardware.
Action
- Check the server LEDs to see if any statuses indicate the source of the issue.
- Power down and disconnect power to the server. Remove all power sources to the server.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Reduce the server to the minimum hardware configuration by removing all cards or devices that are not necessary to power on the server. Keep the monitor connected to view the server power-on process.
- Reconnect power, and then power on the system.
- If the video does not work, check if it is video issue.
Action
- Verify that the server and operating system support the device. For more information, see the server and operating system documentation.
- Be sure the latest device drivers are installed.
- Be sure the device is properly installed. For more information, see the device documentation.
- Uninstall the device.
- If the server works with the device removed and uninstalled, an issue exists with the device, the server does not support the device, or a conflict exists with another device.
- If the device is the only device on a bus, be sure the bus works by installing a different device on the bus.
- Restarting the server each time to determine if the device is working, move the device:
- To a PCIe slot on a different bus
- To the same slot in another working server of the same or similar design
- If you are testing a board (or a device that connects to a board):
- Test the board with all other boards removed.
- Test the server with only that board removed.
- Clearing NVRAM can resolve various issues.
- Verify that the PCIe device or graphics controller does not need additional power to operate. For more information, see the device documentation.
Drives are failed
Action
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Action
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Check to see if an update is available for any of the following:
- RAID Controller firmware
- RAID driver
- Host bus adapter firmware
- Be sure the drive or backplane is cabled properly.
- Be sure the drive data cable is working by replacing it with a known functional cable.
- Be sure drive blanks are installed properly when the server is operating. Drives may overheat and cause sluggish response or drive failure.
- Be sure the replacement drives within an array are the same size or larger.
- Be sure the replacement drives within an array are the same drive type, such as SAS, SATA, or SSD.
- Power cycle the server. If the drive shows up, check to see if the drive firmware needs to be updated.
Symptom
- Drives are not recognized.
- Be sure no power issues exist.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Check for available updates on any of the following components:
- RAID Controller firmware
- RAID driver
- HBA firmware
- Be sure the drive or backplane is cabled properly.
- Check the drive LEDs to be sure they indicate normal function.
- Be sure the drive is supported.
- Power cycle the server. If the drive appears, check to see if the drive firmware needs to be updated.
- Be sure the drive bay is not defective by installing the hard drive in another bay.
- When the drive is a replacement drive on an array controller, be sure that the drive is the same type and of the same or larger capacity than the original drive.
- When using an array controller, be sure the drive is configured in an array.
- Be sure that the correct controller drivers are installed and that the controller supports the hard drives being installed.
Symptom
- The data on the drives is inaccessible.
- The files are corrupt.
- Viruses exist on the server.
- A TPM is installed but not properly enabled on the server.
- Be sure the files are not corrupt. Run the repair utility for the operating system.
- Be sure no viruses exist on the server. Run a current version of a virus scan utility.
- When migrating encrypted data to a new server, be sure to follow the recovery procedures in the operating system documentation.
Symptom
- The server response time is slower than usual.
- The drive is full.
- Operating system encryption technology is causing a decrease in performance.
- A recovery operation is pending on the logical drive.
- Be sure the drive is not full.
- Review information about the operating system encryption technology, which can cause a decrease in server performance. For more information, see the operating system documentation.
RAID Controller drivers are not recognized
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
- When installing an OS, the OS installation does not recognize the RAID Controller drivers.
- Manually install the RAID Controller drivers. For more information, see the controller documentation.
Symptom
- Data failure or disk errors occur on a server with HDD backplane.
- The drive backplane is not cabled properly to the controller.
- Be sure that the drive backplane ports are connected to controller.
General fan issues
Cause
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Cause
- The fans are not seated properly.
- The fan configuration does not meet the functional requirements of the server.
- The server is not ventilated properly.
- One or more required fans are not installed.
- Error messages are displayed during POST.
- One or more fans are not functioning.
- Be sure the fans are properly seated and working:
- Follow the procedures and warnings in the server documentation for removing the access panels and accessing and replacing fans.
- Unseat, and then reseat, each fan according to the proper procedures.
- Be sure the fan configuration meets the functional requirements of the server.
- Be sure no ventilation issues exist.
- Be sure no POST error messages are displayed while booting the server that indicate temperature violation or fan failure information.
- Use BMC WebUI to see if any event list error messages relating to fans are listed.
- In the BMC WebUI interface, navigate to the Sensor page and verify the following information:
- Click the Fans tab and verify the fan status and fan speed.
- Click the Temperatures tab and verify the temperature readings for each location on the
- Temperatures tab. If a hot spot is located, then check the airflow path for blockage by cables and other material.
- A hot spot is not an absolute temperature but is relative to a component specification.
- Replace any required non-functioning fans and restart the server.
- Be sure all fan slots have fans.
- Verify the fan airflow path is not blocked by cables or other material.
Symptom
- The fans are running at a higher speed than expected.
- The system temperature sensor is reading over threshold.
- An air baffle is missing or not installed properly and causing a disruption of the airflow.
- The processor heatsink is not installed as indicated in the server documentation.
- A supported fan is not installed in the server.
- Update the server to the latest firmware versions, such as BMC firmware, system BIOS, option firmware, etc.
- Verify the Temperature tab. Fan speeds can be high if a sensor temperature is over threshold.
- Verify that all air baffles and required blanks, such as drive blanks, processor heatsink blanks, power supply blanks, etc., are installed.
- Verify that the correct processor heatsink is installed.
- Verify that the correct fan is installed.
Symptom
- Fans are operating at high speeds with excessive noise.
- Fans can generate noise if running at a high speed (as expected) or when at low speed if there is an issue with the fan.
- In the BMC WebUI, navigate to the Sensor page.
- Click the Fans tab.
- Verify the fan status and fan speed. Fan speeds greater than 60% are expected to be loud.
- If the fan is running at a speed higher than expected, see "Fans running at a higher than expected speed."
Symptom
- Abnormal/rattling noise observed at low fan speeds might indicate an issue with the fan.
- Replace the fan.
General memory issues
Cause
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Cause
- The memory does not meet server requirements.
- A DIMM has failed.
- Third-party memory is installed on the server.
- The DIMM is not properly seated.
- Isolate and minimize the memory configuration. Use care when handling DIMMs.
- Be sure the memory meets the server requirements and is installed as required by the server. Some servers might require that memory channels be populated fully or that all memory within a memory channel be of the same size, type, and speed.
- If you are unsure which DIMM has failed, test each channel of DIMMs by removing all other DIMMs. Then, isolate the failed DIMM by switching each DIMM in a channel with a known working DIMM.
- Remove any third-party memory.
- To test the memory, run linux stress app.
- Update the BIOS to the latest version.
- Reseat the DIMM.
- Replace the DIMM.
Symptom
- The server is out of memory.
- A POST error message or an IML message is displayed.
- The memory is not configured properly.
- An OS error is indicated.
- Be sure the memory is configured properly. For more information, see the product documentation to determine the memory configuration requirements.
- Be sure no operating system errors are indicated.
- Update the BIOS to the latest version.
Symptom
- A POST error message or an IML message is displayed.
- The DIMM configuration does not support the Memory RAS Configuration setting configured for the server.
- The memory channel was not populated in the correct order.
- An unsupported DIMM is installed in the server.
- The corresponding processor is not installed.
- Verify that the DIMMs are installed according to the DIMM population guides in the server user guide.
- Verify that the Memory RAS Configuration settings and DIMMs are installed according to the DIMM population guidelines in the server user guide.
- Verify that the DIMMs are supported on the server.
- Be sure that the associated processor is installed for all DIMMs on the server.
- Update the BIOS to the latest version.
Symptom
- The server does not recognize new memory installed on the server.
- The memory is not supported on this server.
- The memory is not installed according to the server requirements.
- The memory limits are exceeded for the server.
- The processor is not supported on the server.
- The memory is not installed or seated properly.
- Be sure the memory is the correct type for the server.
- Be sure the memory is installed according to the server requirements.
- Be sure you have not exceeded the memory limits of the server or operating system.
- Be sure no Event List error messages are displayed in the IPMI Event LOG.
- Be sure the memory is seated properly.
- Be sure no conflicts are occurring with existing memory.
- Test the memory by installing the memory into a known working server. Be sure the memory meets
- the requirements of the new server on which you are testing the memory.
- Update the BIOS to the latest version.
- Replace the memory.
Symptom
- A POST error message or a IPMI Event LOG is displayed.
- Stop error or blue screen (Windows)
- Linux kernel panic
- A system “hang”
- A system “freeze”
- Server restarts or powers down unexpectedly
- Parity errors occur
- The DIMM is not installed or seated properly.
- The DIMM has failed.
- Reseat the DIMM.
- Update the BIOS to the latest version.
- If the issue still exists, then replace the DIMM.
Symptom
- Performance is degraded.
- The System Status LED is amber.
- ECC errors occur with no other symptoms.
- The DIMM is not installed or seated properly.
- The DIMM has failed.
- Update the BIOS to the latest version.
- Replace the DIMM.
If you received a POST error message or a IPMI Event LOG, it can be caused by:
- One or more processors are not supported by the server.
- The processor configuration is not supported by the server.
- The server ROM is not current.
- A processor is not seated properly.
- A processor has failed.
- Be sure each processor is supported by the server and is installed as directed in the server documentation. The processor socket requires very specific installation steps and only supported processors should be installed.
- Be sure the BIOS is current.
- Be sure you are not mixing processor stepping, core speeds, or cache sizes if this is not supported on the server.
- If the server has only one processor installed, reseat the processor. If the issue is resolved after you restart the server, the processor was not installed properly.
- If the server has only one processor installed, replace it with a known functional processor. If the issue is resolved after you restart the server, the original processor failed.
- If the server has multiple processors installed, test each processor:
- Remove all but one processor from the server. Replace each with a processor terminator board or blank, if applicable to the server.
- Replace the remaining processor with a known functional processor. If the issue is resolved after you restart the server, a fault exists with one or more of the original processors. Install each processor one by one, restarting each time, to find the faulty processor or processors. At each step, be sure the server supports the processor configurations.
Symptom
- An error message is received indicating low power or loss of power.
- Real-time clock system battery is running low on power or lost power.
- Replace the battery.
Symptom
- A POST message or an BMC WebUI message is received indicating an issue with either the system board or the PDB.
- Review all error messages for possible issues with other components and troubleshoot components identified.
- Verify that no loose connections exist on the system board or PDB. It is not necessary to reseat processors.
- Remove any components recently added.
- Power down and remove all power from the server. Remove the system battery for 10 minutes.
- Reinstall the battery and power on the server.
- Gather necessary information and contact support.
Cause
- The USB drive key is not enabled in the UEFI System Utilities.
- The drive boot order is not set to boot from the USB drive key.
- The USB drive key is not seated properly.
- Be sure that USB is enabled in the UEFI System Utilities.
- Be sure the drive boot order in the BIOS Setup Menu is set so that the server boots from the USB drive key.
- Reseat the USB drive key.
- Move the USB drive key to a different USB port, if available.
System does not boot from the CD-ROM or DVD drive
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
- The system does not boot from the USB CD-ROM or DVD drive.
- The USB CD-ROM or DVD drive is not enabled in the UEFI System Utilities.
- The drive boot order is not set to boot from the USB CD-ROM or USB DVD drive.
- The USB CD-ROM or DVD drive is damaged.
- The USB CD-ROM or DVD drive is not connected or cabled properly.
- Be sure the drive boot order in the BIOS Setup Menu is set so that the server boots from the USB CD-ROM or DVD drive first.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Be sure the media from which you are attempting to boot is not damaged and is a bootable USB CD-ROM or DVD drive.
- Be sure legacy support for a USB CD-ROM or DVD drive is enabled in BIOS Setup Menu.
Symptom
- The data from the CD-ROM or DVD drive is inconsistent or cannot be read.
- The CD or DVD has material or residue on the surface.
- The CD or DVD is not valid for the drive.
- Clean the drive and media.
- If a paper or plastic label has been applied to the surface of the CD-ROM or DVD in use, remove the label and any adhesive residue.
- Be sure the inserted CD or DVD format is valid for the drive. For example, be sure you are not inserting a DVD into a drive that supports only CDs.
Symptom
- The USB CD-ROM or DVD drive is not detected.
- The USB CD-ROM or DVD drive is not cabled properly.
- The USB CD-ROM or DVD drive cables are not connected properly.
- The USB CD-ROM or DVD drive cable is faulty.
- The driver is not correct and needs to be updated.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Be sure cables are connected as required. For more information, see the USB CD-ROM or DVD drive documentation or the server documentation.
- Be sure the cables are working properly. Replace with known functional cables to test whether the original cables are faulty.
- Be sure the correct, current driver is installed.
Troubleshooting general graphics and video adapter issue
Cause
Cause
- The graphics or video adapter is not supported on the server.
- Insufficient power to support the graphics or video adapter.
- The graphics or video adapter is not installed or seated properly.
- Use only cards listed as a supported option for the server.
- Be sure that the power supplies installed in the server provide adequate power to support the server configuration. Some high-power graphics adapters require specific cabling, fans, or auxiliary power.
For more information about adapter power requirements, see the documentation that ships with the graphics option or see the vendor website. - Be sure the adapter is seated properly.
Screen is blank for more than 60 seconds after you power up the server
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
- The screen is blank for more than 60 seconds after the server powered up.
- The monitor is not receiving power.
- The monitor is not cabled properly.
- The monitor cables are not connected properly.
- The power is not sufficient for a PCIe device or graphics controller installed on the server.
- The video drive is not current.
- Be sure the monitor power cord is plugged into a working grounded (earthed) AC outlet.
- Power up the monitor and be sure the monitor light is on, indicating that the monitor is receiving power.
- Be sure the monitor is cabled to the intended server or KVM connection.
- Be sure no loose connections exist by verifying the following connections:
- For rack-mounted servers, check the cables to the KVM switch and be sure the switch is correctly set for the server. You might need to connect the monitor directly to the server to be sure the KVM switch has not failed.
- For tower model servers, check the cable connection from the monitor to the server, and then from the server to the power outlet.
- Press any key, or enter the password, and wait for a few moments for the screen to activate to be sure the energy saver feature is not in effect.
- Verify that a PCIe device or graphics controller does not need additional power to operate. For more information, see the device documentation.
- Press any key, or enter the password, and wait for a few moments for the screen to activate to be sure the power-on password feature is not in effect. You can also tell if the power-on password is enabled if a key symbol is displayed on the screen when POST completes. If you do not have access to the password, you must disable the power-on password by using the Password Disable switch on the system board.
- Be sure the video driver is current. For driver requirements, see the third-party video adapter documentation.
Symptom
- The monitor does not function properly with energy saver features.
- The monitor does not support energy saver features.
- Be sure the monitor supports energy saver features, and if it does not, disable the features.
Symptom
- The video colors are displayed wrong on the monitor.
- The video cable is not connected securely to the correct port.
- The monitor and KVM switch are not compatible with the video output of the server.
- The video cable is damaged.
- Be sure the 15 pin VGA cable is securely connected to the correct VGA port on the server and to the monitor.
- Be sure the monitor and any KVM switch are compatible with the VGA output of the server.
- Be sure that the VGA cable is not damaged. Replace the cable with a known working cable.
Symptom
- Slow-moving horizontal lines are displayed on the monitor.
- Magnetic field interference is occurring.
- Be sure magnetic field interference is not occurring. Move the monitor away from other monitors or power transformers.
Action
- Be sure no loose connections exist by verifying the following:
- If a KVM switching device is in use, be sure the server is properly connected to the switch.
- For rack-mounted servers, check the cables to the switch box and be sure the switch is correctly set for the server.
- For tower model servers, check the cable connection from the input device to the server.
- If a KVM switching device is in use, be sure all cables and connectors are of proper length and are supported by the switch. See the switch documentation.
- Be sure the current drivers for the operating system are installed.
- Be sure the device driver is not corrupted by replacing the driver.
- Restart the system and check whether the input device functions correctly after the server restarts.
- Replace the device with a known working equivalent device (another similar mouse or keyboard):
- If the issue still occurs with the new mouse or keyboard, the connector port on the system I/O board is defective. Replace the board.
- If the issue no longer occurs, the original input device is defective. Replace the device.
- Be sure the keyboard or mouse is connected to the correct port. Determine whether the keyboard lights flash at POST or the NumLock LED illuminates. If not, change port connections.
- Be sure the keyboard or mouse is clean.
Please follow the instruction below:
- Check the network controller or OCP LAN card LEDs to see if any statuses indicate the source of the issue.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Be sure the correct cable type is used for the network speed or that the correct SFP or DAC cable is used. For dual-port 10 GB networking devices, both SFP ports should have the same media (for example, DAC cable or equivalent SFP+ module). Mixing different types of SFP (SR/LR) on a single device is not supported.
- Be sure the network cable is working by replacing it with a known functional cable.
- Be sure a software issue has not caused the failure. For more information, see the operating system documentation.
- Be sure the server and operating system support the controller.
- Be sure the controller is enabled in BIOS.
- Be sure the BIOS is up to date.
- Be sure the controller drivers are up to date.
- Be sure a valid IP address is assigned to the controller and that the configuration settings are correct.
Kindly follow the instruction below to isolate problem:
- Check the network controller or OCP LAN card LEDs to see if any statuses indicate the source of the issue.
- Be sure the correct network driver is installed for the controller and that the driver file is not corrupted. Reinstall the driver.
- Be sure no loose connections exist.
- Be sure the network cable is working by replacing it with a known functional cable.
- Be sure the network controller or FlexibleLOM is not damaged.
Kindly follow the instruction below to isolate problem:
- Scan for viruses with an updated virus scan utility.
- Review the BMC WebUI event log.
- Review the IPMI Event LOG.
- Gather the NMI Crash Dump information for review, if needed.
- Obtain the IPMI Event LOG for use when contacting support.
Symptom
- Error messages are displayed in the error log.
- Follow the information provided in the error log. For more information, see the operating system documentation.
Symptom
- Issues occur after the installation of a service pack.
- Update the operating system. For more information, see "Updating the operating system."
- Before updating the operating system, read the release notes for each update.
- Use care when applying operating system updates (Service Packs, hotfixes, and patches). If you do not require specific fixes from the update, recommend that you do not apply the updates.
If you decide to apply an operating system update:
- Perform a full system backup.
- Apply the operating system update, using the instructions provided.
- Install the current drivers.
If all other options have not resolved the issue, consider reconfiguring the system. Before reconfiguring the system, do the following:
- Weigh the projected downtime of a software reload against the time spent troubleshooting intermittent issues. It might be advantageous to start over by removing and reinstalling the software with issues.
- Be sure the server has adequate resources (processor speed, hard drive space, and memory) for the software.
- Be sure the server BIOS is current and the configuration is correct.
- Be sure you have printed records of all troubleshooting information you have collected to this point.
- Be sure you have two good backups before you start. Test the backups using a backup utility.
- Check the operating system and application software resources to be sure you have the latest information.
- If the last-known functioning configuration does not work, try to recover the system with operating system recovery software. For more information, see the operating system documentation.
If you recently upgraded the operating system or software and cannot resolve the issue, try restoring a previously saved version of the system. Before restoring the backup, make a backup of the current system. If restoring the previous system does not correct the issue, you can restore the current set to be sure you do not lose additional functionality.
For more information, see the documentation provided with the backup software.
For more information, see the documentation provided with the backup software.
Cause
- The software might be incompatible with other software on the server.
- Known issues might exist with the software.
- The server configuration might have changed.
- The server might be infected by a virus.
- Check the application log and operating system log for entries indicating why the software locked up.
- Check for incompatibility with other software on the server.
- Check the support website of the software vendor for known issues.
- Review log files for changes made to the server that might have caused the issue.
- Scan the server for viruses with an updated virus scan utility.
Symptom
- The system locks up after settings were changed.
- The new system settings are not supported.
- Check the system logs to determine what changes were made, and then change the settings back to the original configuration.
Please change the settings back to the original configuration. If more than one setting was changed, change the settings one at a time to isolate the cause of the issue.
Symptom
- Errors occur after an application is installed on a server.
- Check the application log and operating system log for entries indicating why the software failed.
- Check system settings to determine if they are the cause of the error. You might need to obtain the settings from the server setup utility and manually set the software switches. For more information, see the application documentation, the vendor website, or both.
- Check for overwritten files. To determine which files are added by the application, see the application documentation.
- Reinstall the application.
- Be sure you have the most current drivers.
Network connection fails on remote communication by WebUI
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
- An error message describing the broken connection displays and the program exits.
- Because network connectivity cannot be guaranteed, it is possible for the administrative client to become disconnected from the target server during the BIOS or BMC Firmware flash preparation. If any remote connectivity procedure fails during the BIOS or BMC Firmware flash online preparation, the flash does not occur for the target system.
- Attempt to ascertain and correct the cause of connection failure.
- Restart the process.
Symptom
- The server will not start.
- The flash cannot be interrupted during BIOS or BMC Firmware flash, or the BIOS or BMC Firmware image is corrupted and the server does not start. The most likely reason for failure is a loss of power to the system during the flash process.
- Try the flash process again.
- For BIOS flash process stop caused by power loss and cannot boot again, try BIOS recovery process.
- Contact for repairing process if still not work.
Symptom
- If the target system is not listed in the supported servers list, an error message appears and the program exits.
- Only supported systems can be upgraded using the BMC WebUI.
- To determine if the server is supported, check BIOS or BMC Firmware release note and confirm the server model.
Symptom
- The server does not boot.
- The system BIOS or BMC Firmware flash process fails.
- The system ROM is corrupt.
- The server fails to boot after a BIOS or BMC Firmware update using update tool or BMC WebUI.
- A logical drive is not configured on the RAID controller.
- The controller boot order is not set properly.
- RAID containing multiple logical drives might require the boot logical drive to be selected under Option ROM.
- For BIOS flash process fail cause server does not boot, try to use BMC WebUI to update BIOS again.
- BIOS Recovery process.
- For BMC Firmware process fail cause server doesn’t boot, contact for repairing process.
- A logical drive is not configured on the RAID controller. Configure logical drive on RAID controller and set controller boot order properly.
- Properly select boot logical drive under Option ROM when RAID containing multipul logical drives.